大数据软件生态分为三方面:
- 数据存储:Hadoop HDFS, HBase, KUDU, 阿里云 OSS, AWS S3
- 数据计算:Hadoop MapReduce, Hive, Spark, Flink
- 数据传输:Kafka, Pulsar, Flume, Sqoop
Hadoop 是一个大数据整体解决方案,包括三大组件:分布式数据存储 HDFS,分布式数据计算 MapReduce 和分布式资源调度 YARN。本科的时候就做过 Hadoop 实验,几年之后对 Hadoop 是啥都几乎没概念了,刚好又需要做个实验,就记录一下实验过程,从简单的 URLs 统计看 Hadoop 和 HDFS 的基本功能。
本实验在虚拟机 VirtualBox 中完成,系统镜像为 Ubuntu。
虚拟机集群部署#
准备虚拟机#
首先准备三台虚拟机,主机名和配置如下。
| 节点 | CPU | Mem |
|---|
| ubuntu-server-0 | 1 | 4GB |
| ubuntu-server-1 | 1 | 2GB |
| ubuntu-server-2 | 1 | 2GB |
在 Vbox 中将虚拟机网络都配制成桥接模式,以便相互之间可以连通。
设置虚拟机固定 IP,免得重启后发生变动。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
| # 1. 在宿主机上执行,查看 gateway 和 dns
# 本例中 gateway 是 192.168.1.1,dns 是 127.0.0.53
# 查看 gateway 方式 1
$ route -n
Kernel IP routing table
Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface
0.0.0.0 192.168.1.1 0.0.0.0 UG 600 0 0 wlp7s0
192.168.1.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 600 0 0 wlp7s0
# 查看 gateway 方式 2
$ ip route show
default via 192.168.1.1 dev wlp7s0 proto dhcp src 192.168.1.111 metric 600
192.168.1.0/24 dev wlp7s0 proto kernel scope link src 192.168.1.111 metric 600
# 查看 dns 方式 1
$ cat /etc/resolv.conf
...
nameserver 127.0.0.53
options edns0 trust-ad
search .
# 查看 dns 方式 2
$ nslookup www.baidu.com
Server: 127.0.0.53
Address: 127.0.0.53#53
...
# 2. 查看虚拟机当前的 IP,不管是啥我们就固定它了
# 此例中 IP 是 192.168.1.104
$ ip addr
...
2: enp0s3: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 08:00:27:d3:9f:22 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 192.168.1.104/24 brd 192.168.1.255 scope global enp0s3
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fe80::a00:27ff:fed3:9f22/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
...
# 2. 编辑虚拟机的网络配置文件
# 文件原本长这样
$ sudo cat /etc/netplan/00-installer-config.yaml
# This is the network config written by 'subiquity'
network:
ethernets:
enp0s3:
dhcp4: true
version: 2
# 我们把它编辑成这样
$ sudo cat /etc/netplan/00-installer-config.yaml
# This is the network config written by 'subiquity'
network:
ethernets:
enp0s3:
dhcp4: no # 关闭 dhcp
addresses: [192.168.1.104/24] # 虚拟机自己的 IP
gateway4: 192.168.1.1 # 宿主机的 gateway
nameservers:
addresses: [127.0.0.53] # 宿主机的 dns
version: 2
# 3. 让配置生效
$ sudo netplan apply
|
- 配置宿主机和每个虚拟机的
/etc/hosts 免得一直输 IP。
1
2
3
| 192.168.1.104 ubuntu-server-0
192.168.1.105 ubuntu-server-1
192.168.1.106 ubuntu-server-2
|
- 为了安全考虑,在虚拟机中创建 hadoop 用户,专门给 hadoop 用。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| $ sudo useradd -m hadoop -s /bin/bash
# 修改密码
$ sudo passwd hadoop
# 添加 sudo 权限
$ sudo adduser hadoop sudo
# 切换到 hadoop 用户
$ su hadoop
|
- 配置虚拟机之间的 ssh 免密连接,在每台虚拟机上都执行:
1
2
3
4
| $ ssh-keygen -t rsa
$ ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub hadoop@ubuntu-server-0
$ ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub hadoop@ubuntu-server-1
$ ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub hadoop@ubuntu-server-2
|
接下来为了避免不必要的问题,有的教程会让你关闭 firewalld.service 和 SELinux,但是 Ubuntu server 默认都没有这两玩意 ^^;有的教程还会让你安装 ntp 进行时间同步,但是 Ubuntu server 默认就有 time-sync.target,所以也不需要了。
- 给虚拟机配置共享文件夹:在 Vbox 的 Settings -> Shared Folders -> Adds new shared folder,填写宿主机的文件夹路径、文件夹名(这个之后要用到)、在虚拟机中的挂载点,最后勾选上 Auto-mount;再进入虚拟机,挂载共享文件夹。
1
2
| # 在 vbox 中完成共享文件夹配置后,在虚拟机中挂载该文件夹
$ mount -t vboxsf shared-folder /mnt
|
接下来的操作全部在虚拟机中完成,且未说明的话默认每台虚拟机都要进行相同的操作。
配置 Hadoop 依赖环境#
Hadoop 的安装配置详见 Hadoop doc。
- 宿主机下载 Hadoop 的 .tar.gz 压缩包到共享文件夹,进入虚拟机解压缩。
1
| $ tar -zxvf /mnt/hadoop-3.3.6.tar.gz -C ~
|
- 安装依赖软件。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| $ sudo apt install ssh pdsh
# 查看 pdsh 默认使用的 rcmd 类型,需要是 ssh 哦
$ pdsh -q -w localhost
...
Rcmd type rsh
...
# 设置为 ssh
$ echo "export PDSH_RCMD_TYPE=ssh" >> ~/.bashrc
$ source ~/.bashrc
|
- 安装 JAVA,安装的 JAVA 版本根据 Hadoop 版本选择,看官方文档 Hadoop Java Versions。
1
2
3
4
5
| # 安装 openjdk
$ sudo apt install openjdk-8-jdk
# 检查 JAVA
$ java -version
|
- 配置
JAVA_HOME 环境变量。
1
2
3
4
5
| $ cd hadoop-3.3.6/
# 查看 java 位置
$ readlink -f $(which java)
/usr/lib/jvm/java-8-openjdk-amd64/jre/bin/java
|
根据上面得到的输出,编辑 etc/hadoop/hadoop-env.sh,添加下面的内容。
1
| export JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/java-8-openjdk-amd64/jre/
|
- 执行
hadoop 测试一下,输出 usage 文档就成功了!
- 把 bin/ 和 sbin/ 加到 PATH 里。
1
2
| $ echo 'export PATH=$PATH:~/hadoop-3.3.6/bin:~/hadoop-3.3.6/sbin' >> ~/.bashrc
$ source ~/.bashrc
|
部署 Hadoop 集群#
HDFS 架构是主从模式,包括三类角色:
- Name Node:主节点。
- Secondary Name Node:主节点辅助。
- Data node:从节点。
这三种角色其实就是三种进程,将它们部署在我们的三个节点上,分配情况如下。
| 节点 | 服务 |
|---|
| ubuntu-server-0 | NameNode, DataNode, SecondaryNameNode |
| ubuntu-server-1 | DataNode |
| ubuntu-server-2 | DataNode |
部署集群需要编辑 etc/hadoop 下的一些配置文件,先认识一下它们。
- hadoop-env.sh: 配置 Hadoop 相关的环境变量,之前已经接触过了。
- workers: 配置有哪些从节点 DataNode。
- core-site.xml: Hadoop 核心配置文件。
- hdfs-site.xml: HDFS 核心配置文件。
- 配置 etc/workers,默认是
localhost,要将整个文件改为以下内容。
1
2
3
| ubuntu-server-0
ubuntu-server-1
ubuntu-server-2
|
- 配置 etc/hadoop/core-site.xml 如下。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| <configuration>
<property>
<name>fs.defaultFS</name>
<value>hdfs://ubuntu-server-0:8020</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>io.file.buffer.size</name>
<value>131072</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>hadoop.http.staticuser.user</name>
<value>hadoop</value>
</property>
</configuration>
|
fs.defaultFS: 整个 HDFS 内部的网络通讯地址,为 hdfs:// 协议。此处配置表明 NameNode 就位于 ubuntu-server-0 上,DataNode 将和这台虚拟机的 8020 端口通讯。io.file.buffer.size: io 文件缓冲区大小,131072 bit = 16 KB。hadoop.http.staticuser.user: 更改 Hadoop web 界面的默认登陆用户为 hadoop,否则之后 web 界面上的用户权限只允许查看信息(这是为了安全考虑,因此建议不要配置这个选项,这里配置它只是为了体验尝鲜)。
- 配置 etc/hadoop/hdfs-site.xml。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| <configuration>
<property>
<name>dfs.namenode.name.dir</name>
<value>/data/nn</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>dfs.namenode.hosts</name>
<value>ubuntu-server-0,ubuntu-server-1,ubuntu-server-2</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>dfs.namenode.handler.count</name>
<value>100</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>dfs.blocksize</name>
<value>268435456</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>dfs.datanode.data.dir.perm</name>
<value>700</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>dfs.datanode.data.dir</name>
<value>/data/dn</value>
</property>
</configuration>
|
dfs.namenode.name.dir: NameNode 元数据的存储位置。dfs.namenode.hosts: NameNode 允许哪几个 DataNode 连接(即加入集群)。dfs.namenode.handler.count: NameNode 处理的并发线程数。dfs.blocksize: HDFS 默认块大小,268435456 B = 256 MB。dfs.datanode.data.dir.perm: HDFS 默认创建的文件权限设置。dfs.datanode.data.dir: DataNode 的数据存储目录。
既然配置了 dfs.namenode.name.dir 和 dfs.datanode.data.dir,就需要创建配置的这两个目录。
1
2
3
4
5
6
| # 在 ubuntu-server-0 执行
$ mkdir -p /data/nn
$ mkdir -p /data/dn
# 在 ubuntu-server-1 和 ubuntu-server-2 执行
$ mkdir -p /data/dn
|
- 我们之后将以 hadoop 用户身份启动 Hadoop,所以更改一下要用到的目录所属。
1
| $ sudo chown -R hadoop:hadoop /data/ ~/hadoop-3.3.6/
|
- 至此前期准备工作就完成了,现在对整个文件系统进行初始化。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| # 在 ubuntu-server-0 执行
$ hadoop namenode -format
...
/************************************************************
SHUTDOWN_MSG: Shutting down NameNode at ubuntu-server-0/192.168.1.104
************************************************************/
# 执行完后可以看到 /data/nn 里有数据了
$ ls /data/nn/
current
|
- 给虚拟机照个快照吧,保存来之不易的劳动成果(不需要关机)。
HDFS 集群,启动!#
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| # 在 ubuntu-server-0 上执行
$ start-dfs.sh
Starting namenodes on [ubuntu-server-0]
Starting datanodes
localhost: Warning: Permanently added 'localhost' (ED25519) to the list of known hosts.
Starting secondary namenodes [ubuntu-server-0]
# 查看运行的 JAVA 进程,果然符合我们的配置(到另外两台虚拟机上执行也可以看到有 DataNode 进程)
$ jps
3541 NameNode
3836 SecondaryNameNode
3661 DataNode
4111 Jps
# 查看集群状态,可以看到 Live datanodes 有 3 台!(刚启动可能要等一会)
$ hdfs dfsadmin -report
|
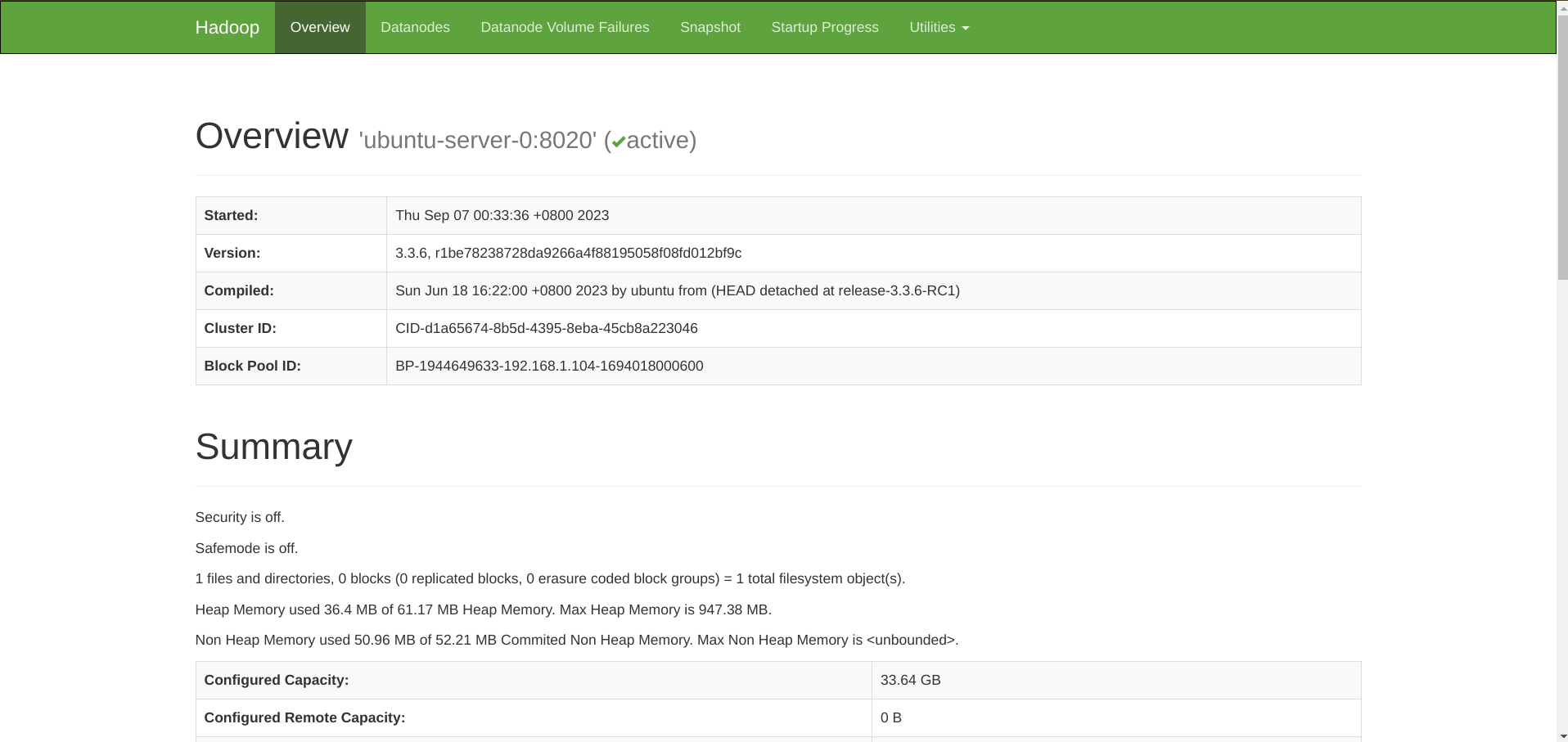
至此就集群就成功拉起了!用浏览器访问 http://ubuntu-server-0:9870 可以看到 Hadoop 的 dashboard。
1
2
| # 关闭 HDFS 集群,在 ubuntu-server-0 执行就行
$ stop-dfs.sh
|
HDFS 基础操作#
一键启动 HDFS 集群。
执行原理:
- 在执行此脚本的主机上启动 SecondaryNameNode。
- 读取 core-site.xml 中的 fs.defaultFS 配置项,启动 NameNode。
- 读取 workers 内容,启动所有 DataNode。
一键关闭 HDFS 集群。
执行原理:
- 在执行此脚本的主机上关闭 SecondaryNameNode。
- 读取 core-site.xml 中的 fs.defaultFS 配置项,关闭 NameNode。
- 读取 workers 内容,关闭所有 DataNode。
还可以单独控制所在主机的进程的启停。
1
| $ hdfs --daemon [start|status|stop] [namenode|secondarynamenode|datanode]
|
查看帮助。
1
2
| $ hdfs --help
$ hdfs dfs -help | less
|
查看文件。
1
2
3
4
5
| # 旧方式
$ hadoop fs -ls <path>
# 或新方式
$ hdfs dfs -ls <path>
|
创建文件夹。默认可以省略协议头,如 hdfs dfs -mkdir /bigdata 和 hdfs dfs -mkdir hdfs://ubuntu-server-0:8020/bigdata 等效。
1
2
| $ hadoop fs -mkdir [-p] <path>
$ hdfs dfs -mkdir [-p] <path>
|
上传文件。
1
2
| $ hadoop fs -put <localsrc> <dst>
$ hdfs dfs -put <localsrc> <dst>
|
下载文件。
1
2
| $ hadoop fs -get <src> <localdst>
$ hdfs dfs -get <src> <localdst>
|
查看文件内容。
1
2
| $ hadoop fs -cat <file>
$ hdfs dfs -cat <file>
|
复制文件。
1
2
3
| # <src> 和 <dst> 都是 HDFS 中的文件
$ hadoop fs -cp <src> <dst>
$ hdfs dfs -cp <src> <dst>
|
修改文件(只支持追加内容)。
1
2
| $ hadoop fs -appendToFile <localsrc> <dst>
$ hdfs dfs -appendToFile <localsrc> <dst>
|
移动文件。
1
2
| $ hadoop fs -mv <src> <dst>
$ hdfs dfs -mv <src> <dst>
|
删除文件。-skipTrash 指跳过回收站直接删除,回收站功能默认关闭,要在 core-site.xml 中配置开启。
1
2
| $ hadoop fs -rm [-r] [-skipTrash] <path>
$ hdfs dfs -rm [-r] [-skipTrash] <path>
|
HDFS 文件权限。注意 HDFS 中最高权限用户是启动 namenode 的用户,所以即使是 root 在操作 HDFS 文件时也可能遇到权限不足的问题。
1
2
3
4
5
| $ hadoop fs -chown
$ hadoop fs -chmod
$ hdfs dfs -chown
$ hdfs dfs -chmod
|
HDFS 存储原理#
将一个文件分为多个固定大小的 block(上面我们配置的 256 MB)存储在不同的 DataNode 上,同时每个 block 都有多个副本(副本数包括本身,默认为 3)存储在其他节点上作备份,空间浪费了但是安全性和读写速度都提升了。
在每一个节点的 etc/hadoop/hdfs-site.xml 中配置默认副本数量。
1
2
3
4
| <property>
<name>dfs.replication</name>
<value>3</value>
</property>
|
检查文件副本数。
1
| $ hdfs fsck <path> -files -blocks -locations
|
那么 Hadoop 是如何记录和整理文件和 blocks 的关系呢?通过 NameNode 的元数据,即之前配置的 dfs.namenode.name.dir。
同时 edits 文件中记录了所有对文件系统的操作,影响的文件和对应的 block,合并 edits 文件即可得到当前的状态。
基于 MR 的 URLs 统计实验#
- 为了能够方便地构建 URLs 模拟数据集,我编写了一个 bash 脚本 urls.sh 来随机生成指定行数的模拟数据。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
| #!/bin/bash
URLs=(
"https://www.google.com"
"https://www.baidu.com"
"https://bing.com"
"https://github.com"
"https://www.bilibili.com"
"https://wiki.archlinux.org"
"https://huggingface.co"
)
LEN=${#URLs[@]}
function help() {
echo -e 'Create a file of specified number of rows containing randomly sorted URLs'
echo -e 'Usage:'
echo -e "\t$0 [-h|--help] [-n|--number NUM] [--] FILE"
}
# parse options
options=$(getopt -o hn: -l help,number: -n "$0" -- "$@")
if [[ -z "$@" || $? -ne 0 ]]; then
help
exit 1
fi
eval set -- "$options"
NUM=0
while true; do
case "$1" in
-n | --number)
shift; # The arg is next in position args
NUM=$1
;;
-h | --help)
help
exit 1
;;
--)
shift
break
;;
esac
shift
done
if ! [[ ${NUM} -gt 0 && ${NUM} =~ ^[0-9]+$ ]]; then
echo "Wrong number of rows"
exit 1
fi
FILE="$@"
# check
if [[ -d $(dirname ${FILE}) && ! -e ${FILE} ]]; then
for ((i=0;i<${NUM};i++)); do
index=$((RANDOM % LEN))
echo ${URLs[index]} >> ${FILE}
done
else
echo "Wrong filepath"
exit 1
fi
echo Created \"$(realpath ${FILE})\"
|
执行该脚本,生成行数参数设定为 10000,数据写入当前目录下的 urls.txt 文件中。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| $ ./urls.sh -n 10000 -- urls.txt
Created "/home/zhao/work/bigdata/urls.txt"
$ head -n 5 ./urls.txt
https://huggingface.co
https://www.baidu.com
https://github.com
https://www.bilibili.com
https://huggingface.co
|
可见该数据集每一行即为一个 URL。
- 编写 mapper.py 和 reducer.py。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
| # mapper.py
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import sys
for line in sys.stdin:
line = line.strip()
print("%s\t%s" % (line, 1))
# reducer.py
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import sys
from operator import itemgetter
current_url = None
current_count = 0
url = None
for line in sys.stdin:
line = line.strip()
url, count = line.split('\t', 1)
try:
count = int(count)
except ValueError:
continue
if current_url == url:
current_count += count
else:
if current_url is not None:
print("%s\t%s" % (current_url, current_count))
current_url = url
current_count = count
if current_url is not None:
print("%s\t%s" % (current_url, current_count))
|
可以先在本机简单实验一下。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| $ cat urls.txt | python mapper.py | sort -k1,1 | python reducer.py
https://bing.com 1469
https://github.com 1432
https://huggingface.co 1414
https://wiki.archlinux.org 1447
https://www.baidu.com 1447
https://www.bilibili.com 1365
https://www.google.com 1426
|
- 将数据上传 HDFS:
hdfs dfs -put ./urls.txt /bigdata/。 - 上传并执行 mapper.py 和 reducer.py。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| $ hadoop jar share/hadoop/tools/lib/hadoop-streaming-3.3.6.jar -files /mnt/mapper.py,/mnt/reducer.py -mapper "python3 mapper.py" -reducer "python3 reducer.py" -input /bigdata/urls.txt -output /bigdata/res/
# 查看 HDFS
$ hdfs dfs -ls -R /
drwxr-xr-x - hadoop supergroup 0 2023-09-07 18:17 /bigdata
drwxr-xr-x - hadoop supergroup 0 2023-09-07 18:17 /bigdata/res
-rw-r--r-- 3 hadoop supergroup 0 2023-09-07 18:17 /bigdata/res/_SUCCESS
-rw-r--r-- 3 hadoop supergroup 191 2023-09-07 18:17 /bigdata/res/part-00000
-rw-r--r-- 3 hadoop supergroup 222529 2023-09-07 17:18 /bigdata/urls.txt
|
- 查看结果。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| # 和之前在本机实验的结果一样!
$ hdfs dfs -cat /bigdata/res/part-00000
https://bing.com 1469
https://github.com 1432
https://huggingface.co 1414
https://wiki.archlinux.org 1447
https://www.baidu.com 1447
https://www.bilibili.com 1365
https://www.google.com 1426
|
